DWTT – Drop Weight Tear Test
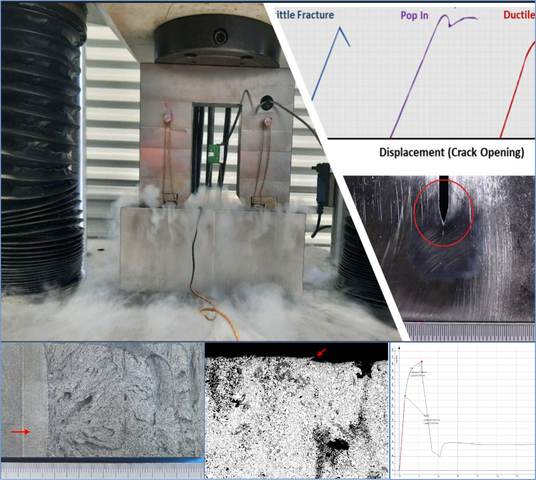
LMATS offers Drop-Weight Tear Test (DWTT) via an international partner laboratory. DWTT is a common test method to assess fracture properties of steel. Its fundamental purpose is to determine the appearance of propagating fractures in steels over the temperature range where the fracture mode changes from brittle to ductile.
The DWTT specimen is of the full material thickness (but up to 19mm only), contains a shallow pressed notch and is loaded in three-point bending. A series of specimens is broken under impact loading at a variety of temperatures, and the proportions of ductile fracture (shear) and cleavage on the fracture surfaces are measured.
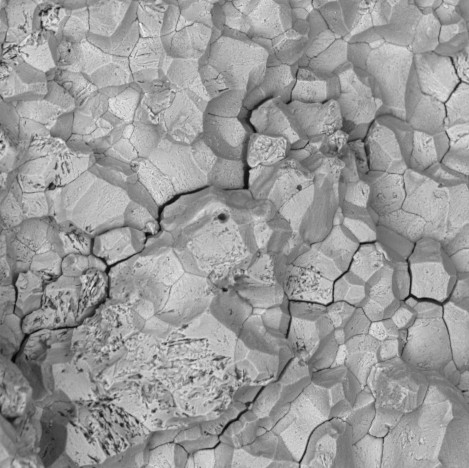
The broken sample from the DWTT is inspected to determine the percentage of the area that failed by shear fracture, called the shear appearance. When this value is 85% or more (Battelle criterion) the steel is supposed to have sufficient toughness and will not exhibit brittle fracture behavior in full-scale conditions.
The temperature at which this threshold is reached is called the shear appearance transition temperature and is assumed to have a very good match with the Fracture Propagating Transition Temperature (FPTT) of an actual pipeline.