Tensile Tests
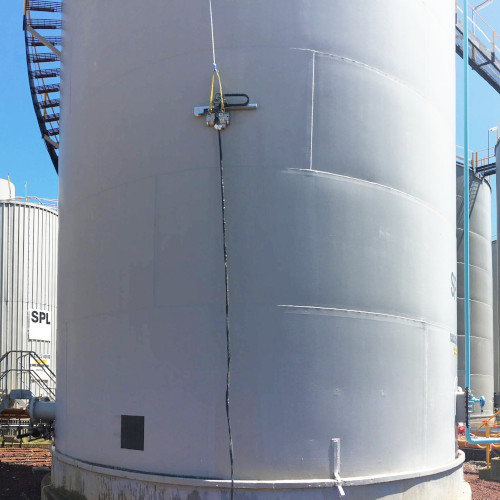
Machined tensile tests are used to determine specific mechanical properties of the test specimen, including tensile strength, yield strength, elongation and reduction of area. Standard sized specimens are typically machined from a sample of the material and loaded in a controlled manner within the parameters of the standard test method. Transverse joint tensile tests are used to determine the tensile strength of a welded joint, comprising of the weld metal, heat affected zone and base material.
All-weld metal tensile tests are used to measure the mechanical properties of the weld metal from a joint in isolation from the base material. These mechanical properties include tensile strength, yield strength, elongation and reduction of area. Through thickness (Z-section or Z-axis) tensile tests are designed to test the ductility of rolled steel through the Z-axis of the specimen. These coupons should have a low sulphur content (<0.01%) to ensure compliance to the relevant standard.
The Full-size Axial tensile test of bolts, screws and threaded bars is an axial tensile test used to determine the strength of an externally threaded fastener as a component.
Wedge Tensile Tests are performed on bolts and other fasteners with fully formed heads. The test identifies the strength of the fastener in tension but also the soundness of the head. Forging issues and poorly made under head radiuses can cause the bolt to fail prematurely. Tensile tests of stainless steel threaded fasteners are used to determine specific mechanical properties of the finished component, including tensile strength, 0.2% proof load and elongation. Wire Tensile Tests: Individual strands, wires or full wire ropes can be tested. Wire rope material can be steel, copper, aluminium or other alloys.